Marthe J. Howard, Ph.D.

Professor Emerita
Email: marthe.howard@utoledo.edu
Education:
1973: B.A., University of California, Berkeley
1978: M.A., California State University, San Francisco
1984: Ph.D., University of California, Irvine
Research Interests:
The work in my laboratory focuses on growth and transcription factor regulation in the specification and differentiation of autonomic neurons. We use modern molecular biology and cell biology techniques to assess gene regulation in avian and mouse embryos. The overall goal of our studies is: 1) to identify genetic regulatory networks involved in neurogenesis and expression of neurotransmitter molecules, 2) to identify cell extrinsic signaling molecules involved in neurogenesis, and 3) to understand the interplay between cell extrinsic cues and cell intrinsic patterns of gene regulation resulting in differentiation of autonomic neurons. Howard's lab is funded by the National Institute of Health (NIDDK, NINDS).
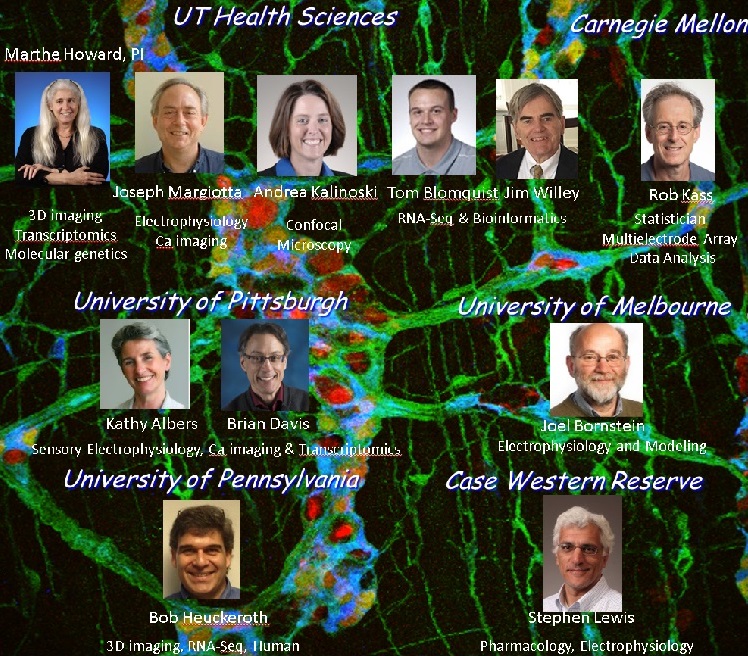
The Howard research consortium includes investigators from the University of Toledo, The University of Pittsburgh, Carnegie Mellon University, Melbourne University, the University of Pennsylvania and Case Western Reserve University (See Figure).
Research Techniques:
1) Molecular Biology techniques including cloning, RNA & DNA purification and analysis, RT-PCR, EMSA, transient transfection, gene array analysis, ChIP assays, mouse genetic manipulation; 2) Cell Biology techniques including cell and tissue culture, immunocytochemistry, histochemistry, Western blot analysis, biochemical pull-down assays, in ovo electroporation; 3) Image analysis including confocal microscopy.
Research Summary:
A challenge in developmental neurobiology is to delineate the molecular mechanisms governing diversification of neuronal phenotypes developing from multipotent progenitor cells. The neural crest is a multipotent progenitor population of cells that gives rise to a diverse array of cell types including neurons, bone, and muscle. We have employed the neural crest as a model system for our studies of growth and transcription factor influences on the specification and phenotypic expression of sympathetic and enteric neurons. Neurons comprising the peripheral nervous system are derived from neural crest cells and are quite diverse in their phenotypic characteristics. Growth factors and transcriptional regulators together control the development of specific
We previously examined the requirements for growth factors in the differentiation of noradrenergic and cholinergic neurons from neural crest-derived precursors. Our early studies in avians demonstrated that the neural tube synthesizes and secretes a small protein growth factor required by neural crest-derived cells to differentiate as NE neurons but not as cholinergic neurons (Howard and Bronner-Fraser, 1985;1986; Howard, 1987). We showed that there is a critical period, during the early migration and localization of crest-derived cells, in which they must be exposed to this factor in order to differentiate as NE neurons (Howard and Gershon, 1991). We identified the neural tube-derived factor as a member of the TGF- b superfamily (Howard and Gershon 1991). Work from several laboratories suggests that the factor is BMP. In addition to soluble factors which can influence the differentiation of neural crest-derived cells, we have identified a non-integrin laminin binding protein expressed on migrating neural crest-derived cells in the enteric anlage required for the cessation of migration and subsequent expression of neuronal phenotypic characteristics (Howard and Gershon, 1996).
Both cell extrinsic and cell intrinsic signals are required for the diversification and phenotypic expression of subtype specific characteristics by neural crest-derived cells. In collaboration with my husband, Dr. Joseph Margiotta, we showed that all classes of neural crest-derived neurons express neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptors (AChR’s). While it is clear that expression of neurotransmitter phenotypic characteristics is dependent upon cell extrinsic signals, the expression of neurotransmitter receptors does not appear to depend on growth factor signaling (Howard et al., 1995). Neural crest-derived cells begin to express transcripts encoding subunits of nAChR’s during their migration from the neural tube and with the exception of transcripts encoding a7, their expression is maintained for at least 12 days in culture (Howard et al., 1995).
We recently cloned two novel members of the basic helix-loop-helix (bHLH) DNA binding factor family called HAND2 and HAND1 (Howard et al., 1999). The expression of these two genes, in neurons, is restricted to neural crest-derived sympathetic and enteric ganglia exclusively. This is a very restricted pattern of expression compared to other bHLH transcription factors shown to be important in aspects of neurogenesis. HAND2 is expressed in some migrating neural crest-derived cells suggesting an early role in cell-type specification. In addition to their expression in sympathetic and enteric ganglia, HAND genes are expressed in the cardiac anlage, limb bud, and branchial arch. (Howard et al., 1999; Wu and Howard, 2002). The spatial and temporal expression patterns of transcripts encoding HAND2 suggested a pivotal role in the specification and/or phenotypic expression of sympathetic and enteric neurons.
Our studies in avian embryos have demonstrated that HAND2 is both sufficient and necessary for the specification and differentiation of peripheral NE neurons (Howard et al., 1999; 2000; Liu and Howard., 2005; Howard, 2005). Using gain-of-function and loss-of-function paradigms, both in vivo and in vitro, we have determined the epistatic relationship between a series of transcriptional activators reguired for different aspects of NE differentiation. BMP4 derived from the dorsal aorta induces expression of the homeodomain DNA binding factor Phox2b which then induces the expression of HAND2 (Howard et al., 2000). HAND2 induces expression of the related homeodomain factor Phox2a. Together, Phox2a and HAND2 regulate transcription of dopamine- b-hydroxylase (DBH) thus expression of norepinepherine (Xu et al., 2003). We have identified a novel mechanism of HAND2 activity at the DBH promoter (Xu et al., 2003) and have demonstrated that post-translational modification of HAND genes
The role that HAND gene products play in development of enteric neurons is less clear than that we have described for specification and differentiation of NE neurons. We have used in-situ hybridization combined with immunocytochemistry to demonstrate that transcripts encoding HAND2 are expressed in enteric neural crest-derived neurons (Wu and Howard, 2002; Hendershot et al., 2006) at all levels of the developing gut. Transcripts encoding HAND1 are confined to the rostral gut and not expressed by neural crest-derived cell types. The differential spatial and temporal patterns of expression of transcripts encoding HAND2 and HAND1 suggest that HAND1 functions in patterning gut architecture while HAND2 functions in the differentiation of enteric neurons (Wu and Howard, 2002; Hendershot et al., 2006). In the developing enteric nervous system, GDNF plays a significant role in specification and differentiation of neural crest-derived cells within the gut microenvironment. The gut synthesizes and secretes a factor that supports the induction of transcripts encoding HAND2 in neural crest-derived precursors of enteric neurons tentatively identified as GDNF (Wu and Howard, 2002). We plan to extend our initial observations and identify growth factors regulating expression of HAND genes in the gut as well as determining the functional significance of their expression.
Most recently, we have generated a targeted null mutation of HAND2 (Hendershot et al., 2006). Disruption of HAND2 expression specifically in neural crest-derived cells demonstrates that HAND2 is required for both neurogenesis and cell type-specific gene
We plan to continue using a combination of molecular and cellular approaches to define the role that the HAND genes play in parlaying the action of growth factors into the expression of genes that confer the specific sympathetic and enteric phenotype of some neural crest derivatives. A better understanding of how neural crest cells become committed to a particular lineage and once committed, how they begin to show cell type-specific gene expression, may greatly enhance our ability to understand how the nervous system develops. We will also expand our studies, through collaboration, to include an analysis of the function of HAND2 in neural crest contribution to cardiogenesis and craniofacial development.
References (Partial List):
Vincentz, J.W., VanDusen, N., Rubart, M., Howard, M.J., Firulli, B.A., Firulli, A.B. (2012). A Phox2- and Hand2-dependent cis-regulatory element regulates Hand1 expression in sympathetic neurons. J. Neurosci. 32: 2110-2120.
Vincentz, J.W., Firulli, B.A., Lin, A., Spicer, D.B., Howard, M.J. and Firulli, A.B. (2012). Twist1 controls a post-migratory cell specification switch that governs cell fate decisions within the cardiac neural crest. PLoS Genet 9(3): e1003405. doi:10.1371/journal.pgen.1003405
Wu, X. and Howard, M.J. 2001. Two Signal Transduction Pathways Involved in the Catecholaminergic Differentiation of Avian Neural Crest-derived Cells In Vitro.Mol. Cell Neurosci. 18:394-406.
Wu, X. and Howard, M.J. 2002. Transcripts Encoding HAND Genes are Differentially Expressed and Regulated by BMP4 and GDNF in Developing Avian Gut. Gene Expression 10:291-305.
Bevan, C., Porter, D., Prasad, A., Howard, M. J., and Henderson, L.P. (2003). Endocrine disrupters alter early development in Xenopus laevis Env. Hlth. Persp. 111:488-496.
Xu, H., Firulli, A.B., Zhang, X. and Howard, M.J., 2003. HAND2 Synergistically Enhances Transcription of Dopamine- b-hydroxylase in the Presence of Phox2a . Dev. Biol. 262:183-193.
Firulli, B.A., Howard, M.J., McDaid, J.R., MciIreavey, I., Cserjesi, P., Virshup, D.M. and Firulli, A, B. 2003. PKA, PKC and the protein phosphatase 2a influence HAND factor function: a mechanism for tissue specific transcriptional regulation . Molec. Cell , 12:1225-1237.
Zhou, X., Nai, Q., Chen, M., Dittus, J.D., Howard, M.J. and Margiotta. J. F. (2004). BDNF and trkB Signaling in Parasympathetic Neurons: Relevance to Regulating Nicotinic Receptors and Synapses. J. Neuroscience 24(18): 4340-4350.
Howard, M.J. (2005). Mechanisms and Perspectives on Differentiation of Autonomic Neurons Dev. Biol. 277:271-286.
Liu, H., Margiotta, J.F and Howard, M.J. 2005. BMP4 Supports Noradrenergic Differentiation by a PKA-dependent Mechanism. Dev. Biol. 286:521-536.
Sarkar, A. and Howard, M.J. Interactions Between Extrinsic and Extrinsic Signaling Molecules in Specification of Noradrenergic Neurons. 2005. Invited Review: International Journal of Autonomic Nervous System. Autonon. Neurosci.Basic and Clinical. 126-127:225-231.
Bevan, C.L., Bryleva, E., Porter, D.M., Hendershot, T., Liu, H., Howard, M.J. and Henderson, L.P. 2006. The endocrine disrupting counpound, Nonylphenol, inhibits neurotrophin-dependent neurite outgrowth via a G protein-dependent mechanism. Endocrinology 147(9):4192-204.
Hendershot, T.J., Liu, H., Sarkar, A.A., Giovannucci, D.R., Clouthier, D.E., ,Abe,M. and Howard, M.J. (2007). Expression of Hand2 is Sufficient for Neurogenesis and Cell Type-specific Gene Expression in the Enteric Nervous System, Dev. Dyn. 236:93-105.
Hendershot,, T.J., Liu, H., Clouthier, D.E., I., Shepherd, Coppola, E., Studer, M., Firulli, A.B., Pittman, D. and Howard, M.J. (2008). Conditional Deletion of Hand2 Reveals Critical Functions in Neurogenesis and Cell Type-specific Gene Expression for Development of Neural Crest-derived Noradrenergic Sympathetic Ganglion Neurons. Dev. Biol. 319:179-191. PMCID: PMC2517160
Schmidt, M., Lin, S., Pape, M., Ernsberger, U., Howard,M. J., and Rohrer, H. (2009).The bHLH transcription factor Hand2 is essential for the maintenance of noradrenergic properties in differentiated sympathetic neurons. Dev. Biol 329; 191-200. PMID: 19254708
Holler, K.L., Hendershot, T.J., Troy, S.E., Vincentz, J.W., Firulli, A.B., and Howard, M.J. (2010). Targeted deletion of Hand2 in cardiac neural crest-derived cells influences cardiac gene expression and outflow tract development. Dev Biol. 341:291-304. PMID: 20144608.
Barron, F., Woods, C., Kuhn, K., Bishop, J., Howard, M.J. and Clouthier, D.E. (2010). Downregulation of Dlx5 and Dlx66 expression by Hand2 is essential for initiation of tongue morphogenesis. Development 138:2249-2259.
Lei, J. and Howard, M.J. (2011). Targeted deletion of Hand2 in enteric neural precursor cells affects its functions in neurogenesis, neurotransmitter specification and gangliogenesis causing functional aganglionosis. Development 138:4789-4800. Reviewed by the Faculty of 1000.
Vincentz, J., VanDusen, N., Rubart, M., Howard, M.J., Firulli, B.A., Firulli, A.B. (2012). A Phox2- and Hand2-dependent cis-regulatory element regulates Hand1 expression in sympathetic neurons. J. Neurosci. 32: 2110-2120.


