James T Slama, Ph.D., CChem MRSC

Distinguised University Professor Emeratus
Department of Medicinal and Biological Chemistry
Frederic and Mary Wolfe Center 274E
Phone: 419.383.1925
E-mail: james.slama@utoledo.edu
Area of Research
My research focuses on the chemical biology of intracellular Ca+2 signaling, and the role of both nicotinic acid adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NAADP) and cyclic adenosine diphosphate ribose (cADP-ribose) as intracellular Ca2+ mobilizing second messengers. We recently developed chemical- enzymatic syntheses of photoactive and “clickable” NAADP analogs which we applied to identify the protein JPT2 as the NAADP binding receptor in culture human cells. We will continue our chemical biological studies to identify NAADP binding proteins in sea urchin egg homogenates and to identify cADP-ribose receptors in cultured mammalian cells.
The general focus of our research is on glycosidases, glycosyltransferases, nucleosidases, and ADP-ribosyl transferases. Each of these enzyme families defines an important area of research and each offers novel opportunities for new drug development. Glycosidases are important in the digestion of carbohydrates
and in the biosynthesis of glycoproteins containing complex carbohydrate chains. Glycosyl transferases utilize nucleoside diphosphate sugars and are responsible for the biosynthesis of complex carbohydrates, glycoproteins, and glycolipids, and in microorganisms for the synthesis of the cell wall. Nucleosidases function in nucleotide and nucleotide salvage pathways targeted by a variety of anticancer, immunosuppressive, and antiprotozoal drugs. Last, ADP-ribosyl transferases catalyze transfer of the ADP-ribose moiety of NAD to a variety of macromolecular acceptors. The functions of ADP-ribosyl transfer reactions are poorly understood, but roles in cell regulation seems likely. Compounds that target ADP-ribosyl transfer reactions could therefore constitute a new class of drugs.
Our experimental approach combines efforts directed toward the design and synthesis of mechanism based enzyme inhibitors with biochemical studies on targeted enzymes, utilizing both conventional and recombinant DNA-based approaches. The goal is to better understand the metabolism and biological function of each enzyme family and at the same time define the specific enzymatic targets relevant to drug development.
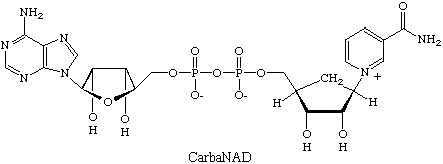
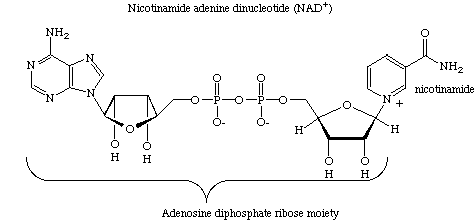
As an example, some of our recent work focuses on studies on ADP-ribosyl transfer
reactions where oxidized nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD) serves as an adenosine
diphosphate ribose (ADP-ribose) donor. CarbaNAD was the first successful designed
inhibitor for this class of enzyme. In carbaNAD a cyclopentane ring replaces the furanose
of the nicotinamide ribonucleoside moiety. CarbaNAD is therefore resistant to nicotinamide
ribotide cleavage but is recognized as a competitive inhibitor by several ADP-ribosyl
transferases.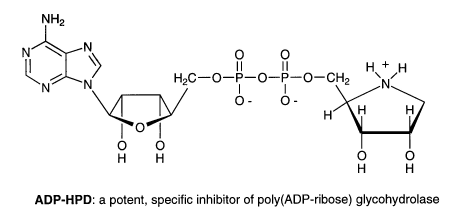
Adenosine diphosphate (hydroxymethyl)pyrrolidinediol (ADP-HPD) is another example
of a successful designed inhibitor. ADP-HPD is a nitrogen-in-the-ring analog of ADP-ribose
and a potent inhibitor of poly(ADP-ribose) glycohydrolase. Poly(ADP-ribose) glycohydrolase
catalyzes the degradation of ADP-ribose polymers, which are synthesized in the nucleus
as a response to DNA damage. ADP-HPD will serve as a useful biochemical probe for
deciphering the structure and mechanism of this glycohydrolase. It will also be applied
in ongoing studies to elucidate the function of ADP-ribose metabolism following DNA
damage. Last, it will serve as a lead compound for the development of inhibitors with
improved stability and bioavailability, which may be useful as antitumor drugs.
Educational Background
| Ph.D. in Chemistry | University of California, Berkeley, 1977 |
| A.B. in Chemistry | Cornell University, Ithaca, NY, 1972 |
Training
- Jointly appointed as a faculty member in the Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry, University of Toledo, 2004-present.
- Research Fellow in Pharmacology, Harvard Medical School, 1977-1979
- Research Assistant, Department of Chemistry, University of Chicago, 1979-1982
- Visiting Scientist, Department of Biological Chemistry, University of Michigan Medical School, Ann Arbor, Michigan; Prof Jack E. Dixon, Host, 1999-2000.
Scope of Practice
Research experience in nucleoside and nucleotide chemistry, heteroaromatic chemistry, enzymatic methods in organic synthesis, photoaffinity labeling, “click chemistry” applications, chemical modification of proteins, protein expression, and receptor identification. Teaching and curriculum development in biochemistry, medicinal chemistry, and the pharmaceutical sciences. Higher education administration experience as Director of the B.S. in Pharmaceutical Sciences program.
Awards, Honors and Grants
- R15 GM131329 National Institute of General Medical Sciences. 09/20/2018–08/31/2021
Identification of the Elusive NAADP Receptor
Role: Principal Investigator
Project Narrative: Changes in the intracellular calcium-ion concentration are a fundamental cell regulatory mechanism. Nicotinic acid adenine dinucleotide 2′-phosphate (NAADP) is one of several interacting intracellular 2nd messengers that mobilize calcium-ion to control biological responses. Our goal is to use a chemical and biochemical approach to identify the receptor for NAADP and apply this discovery to better understand this fundamental cell regulatory mechanism. - R15 GM100444 National Institute of General Medical Sciences. 06/01/12-05/31/16
Chemobiologic Approach to NAADP Signaling
Role: Principal investigator
Project Narrative: Changes in intracellular calcium-ion concentration are a fundamental cell regulatory mechanism. Nicotinic acid adenine dinucleotide 2’-phosphate (NAADP) is one of several interacting intracellular 2nd messengers that mobilize calcium-ion to control biological response. Results of this program will enhance our understanding of NAADP signaling mechanisms, identify new therapeutic targets, and uncover novel drug strategies. It will contribute to understanding fertilization, insulin secretion, smooth muscle contraction, and other important processes. - The results of our recent research was presented before the European Calcium Society 18 February 2021 in a virtual symposium. The proceedings of the symposium were summarized in a special article in the Tuesday, 23 March 2021 edition of Science Signaling: Patel, Sandip, Martina Gregori, and Yu Yuan. "Teaming with NAADP." Science Signaling 14, no. 675 (2021).
Issued Patents
- Bachmann, K. A. and J. T. Slama (2006). PXR agonists for cardiovascular disease. U.S. Pat. US 20060211632 A1. University of Toledo, OH USA.
- Bachmann, K. A. and J. T. Slama (2000). Method for increasing HDL cholesterol levels using heteroaromatic phenylmethanes. U.S. Pat. US 6103733 A 20000815. University of Toledo, OH USA.


