CeDER CORE FACILITIES
To examine the role of specific genes in diseases, we generate unique genetically engineered mouse models. To diagnose whether mice develop diabetes and obesity, we depend on rich core facilities. To this end, we have developed an Animal Phenotyping Core and joined a Regional Diabetes Center, administered by the University of Michigan, that makes available at low cost many state-of-the-art services and equipment.
Pathology Core:
CeDER is equipped with a Nikon Eclipse 80i microscope that contains a 5 megapixel DS-Fi1 camera, polarizers, and NIS-Elements imaging software to capture high resolution images and sample polarization, and to carry out advanced imaging analysis. Two pathologists, Dr. Cara Gatto-Weis, MD and Meenakshi Kaw, MD/PhD have received training on mouse pathology by completing an online course offered by UC Davis.
Animal Phenotyping Core:
Micro-Computed Tomography Unit:
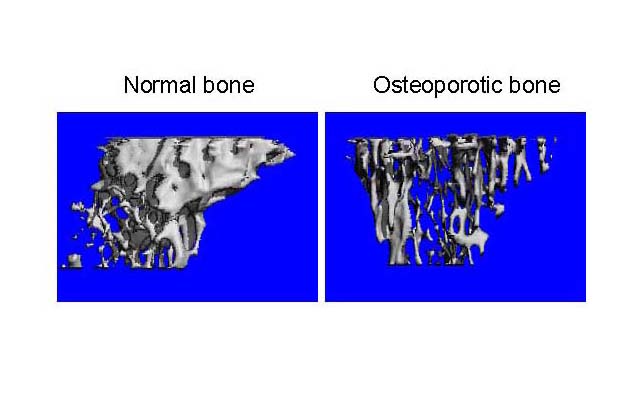
As part of the Bone Biology Laboratory, Dr. Beata Lecka-Czernik oversees the use of a ScancoCT Xray scanner suited for precise analysis of bone architecture
and bone parameters of small rodents. Much like human diagnostics, the computed tomography
unit allows for the monitoring of bone status, including its internal micro-architecture
and strength, in different metabolic disorders and during the process of bone fracture
healing.
  |
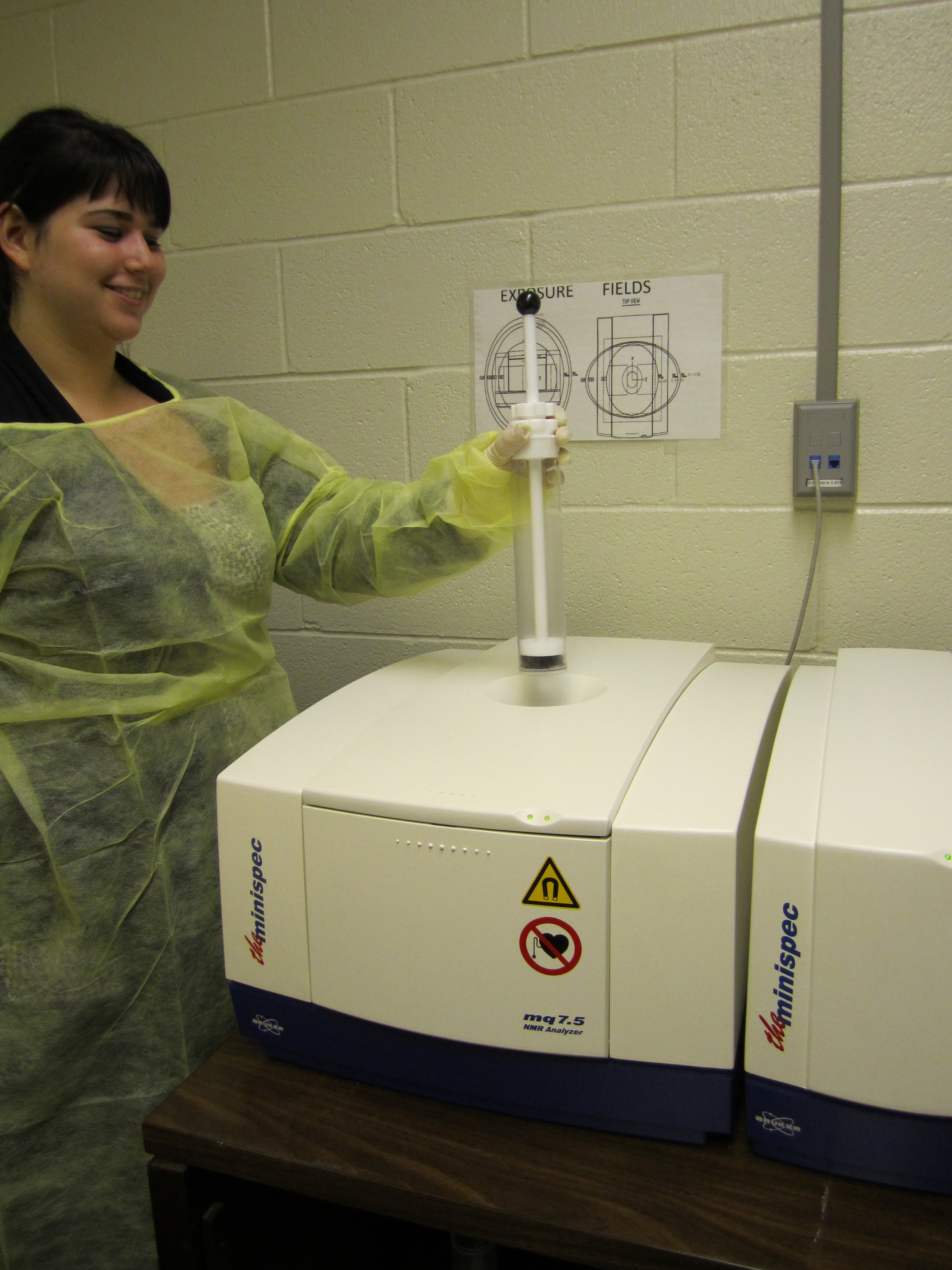
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) Instrument (Bruker Minispec LF50):
This instrument measures body composition parameters, including fat mass, lean tissue
mass and total body water in live mice.
Advantages:
- Rapid measurements- two minutes
- Accuracy
- No need for anesthesia
- Longitudinal evaluation of body fat composition
- Cost-effectiveness: Mice are kept alive for further in vivo phenotypic evaluation

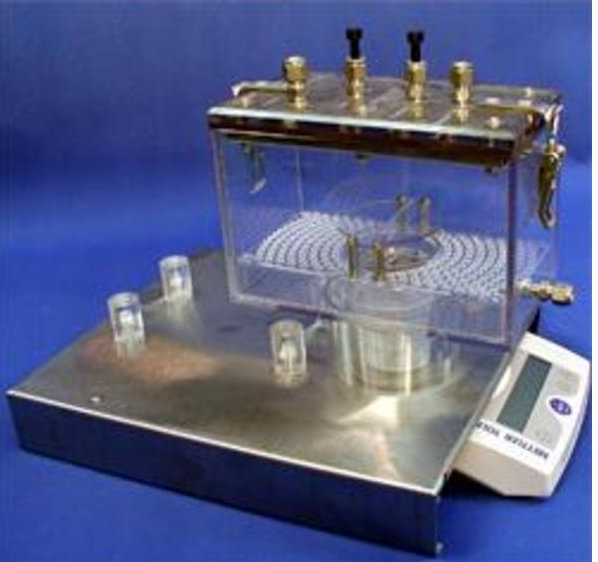
In May, 2012, CeDER purchased 16 metabolic chambers [Columbus Instruments Comprehensive Lab Animal Monitoring System (CLAMS)]. These chambers are capable of monitoring open-circuit calorimetry, activity, feeding, drinking, and sleep detection. Optional features for expansion include monitoring of body mass, food access control, running, urine collection, core body temperature, and heart rate in an optional environmental chamber.
As configured, cages can give up to 96 hours of data on metabolic rate, respiratory quotient, consumption of food and water, spontaneous activity, circadian rhythm, and sleep detection. (The last 3 parameters can also be measured independently through use of separate actigraphy cages, which are also available and are housed in the same room).
Inquiries in regards of using these chambers should be directed to the office of the Director of CeDER (X4183).
 |
 |
Murine Actigraphy Cages
In June, 2011, Dr. Raymond Bourey purchased 16 cages to monitor and record X-Y activity
with frequency of 10 seconds. For ease of use, data are collected and managed by the
same software utilized in the Murine Metabolic Chambers available in the same room.
This apparatus can be used for monitoring locomotion, determination of circadian rhythms,
and detection of sleep bouts.
(Pack AI, Galante RJ, Maislin G, Cater J, Metaxas D, Lu S, Zhang L, Von Smith R, Kay
T, Lian J, Svenson K, Peters LL. Novel method for high-throughput phenotyping of sleep
in mice. Physiol Genomics 28: 232–238, 2007).
Advanced Microscopy and Imaging Center: AMIC Brochure
The University of Toledo Advanced Microscopy & Imaging Center hosts a variety of microscopes
and advanced technologies that assist investigators in developing imaging protocols
for cardiovascular phenotyping. Our technologies, complete with versatile software
packages, allow for simple in vivo or in vitro image acquisition of various organ systems. Specifically, investigators have access
to a Leica TCS SP5 multiphoton laser scanning confocal microscope outfitted with both
conventional and high speed scanners, allowing for excitations lines from 458, 488,
514, 561, 633, and 710-990nm (from the tunable Ti-Sapphire MP laser). This system
is capable of collecting up to 5 colors simultaneously for quantitative confocal image
analysis, 3D reconstruction, FRAP and FRET, animation, stereo imaging, single layer
projection, time lapse collection, and co-localization analysis. In addition, we have
a Total Internal Reflection Fluorescence (TIRF) Microscope coupled to multiple lasers
(488, 546, 633nm) and equipped with a live-cell imaging incubator for time-lapse imaging.
Experiments requiring whole animal fluorescence/bioluminescence imaging are performed
on the IVIS Spectrum (Molecular Devices), a multimodal bioluminescent/fluorescent
imaging system designed for noninvasive imaging of cells and tissues in small animals.
This instrument facilitates the study of biological processes via fluorescence, including
tumor growth, cancer metastasis, bacterial infections, immune responses and inflammation,
and regulation of tissue-specific gene expression. Further, an ACUSON Sequoia TM
C512 cardiac ultrasound imaging system, manufactured by Siemens Medical Solutions
USA, Inc. is also available. This Echocardiography system is widely accepted as a
valuable research tool for studying a broad range of cardiovascular disease processes
in small animals, including ischemic heart disease, heart failure, cardiac hypertrophy
and remodeling, hypertension and diabetic cardiomyopathy. The Sequoia system provides
a full range of echocardiographic capabilities including high-resolution imaging,
tissue harmonic imaging, differential echo amplification, spectral Doppler (Pulsed
and Continuous Wave), color Doppler (for measurements of velocity energy and tissue
Doppler imaging), and M-mode and color-Doppler M-mode imaging. This system is extremely
versatile and ideal for noninvasive imaging of research animal models including rats
and mice. All microscopy and advanced imaging technologies are located in the University
of Toledo Advanced Microscopy & Imaging Center in the Block Health Science Building
room 057. Consultation, training and scheduling for the development of projects within
the cardiometabolic training program are provided by the Technical Director.
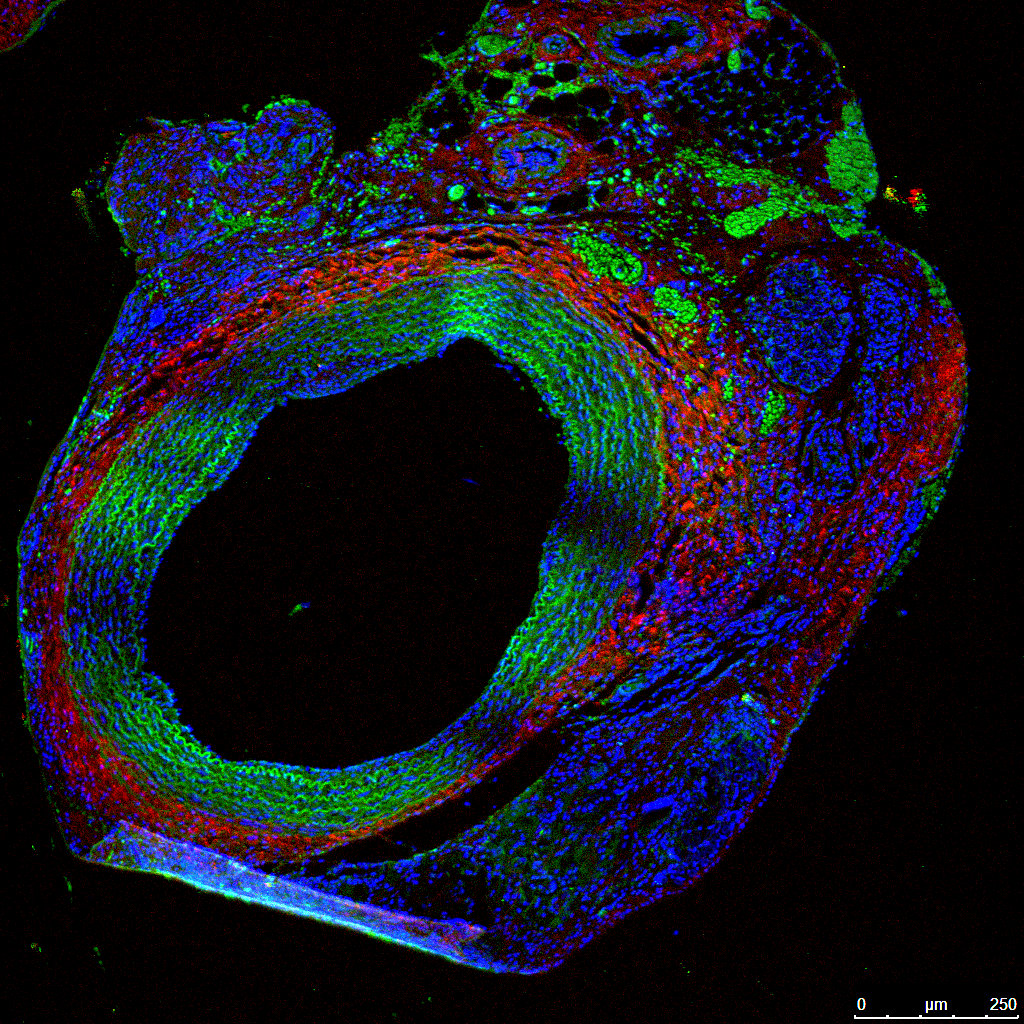
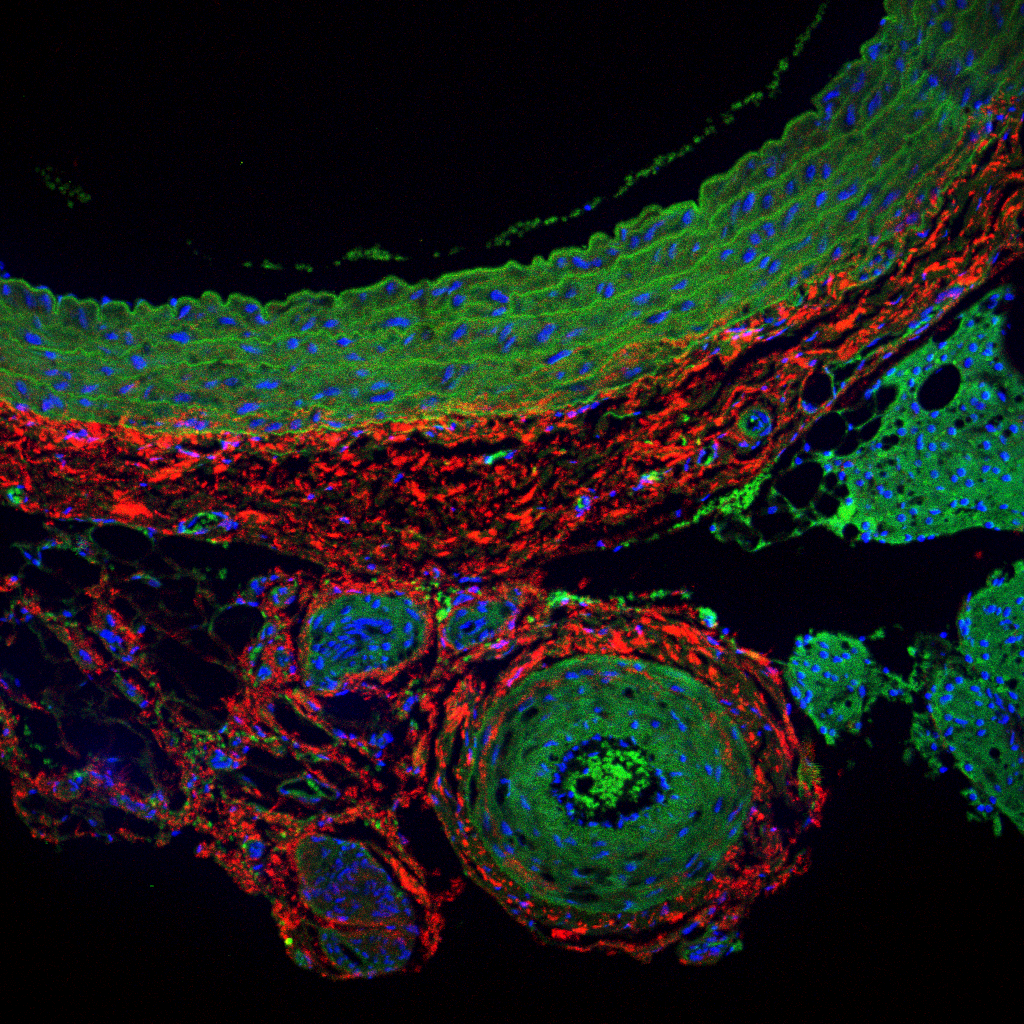
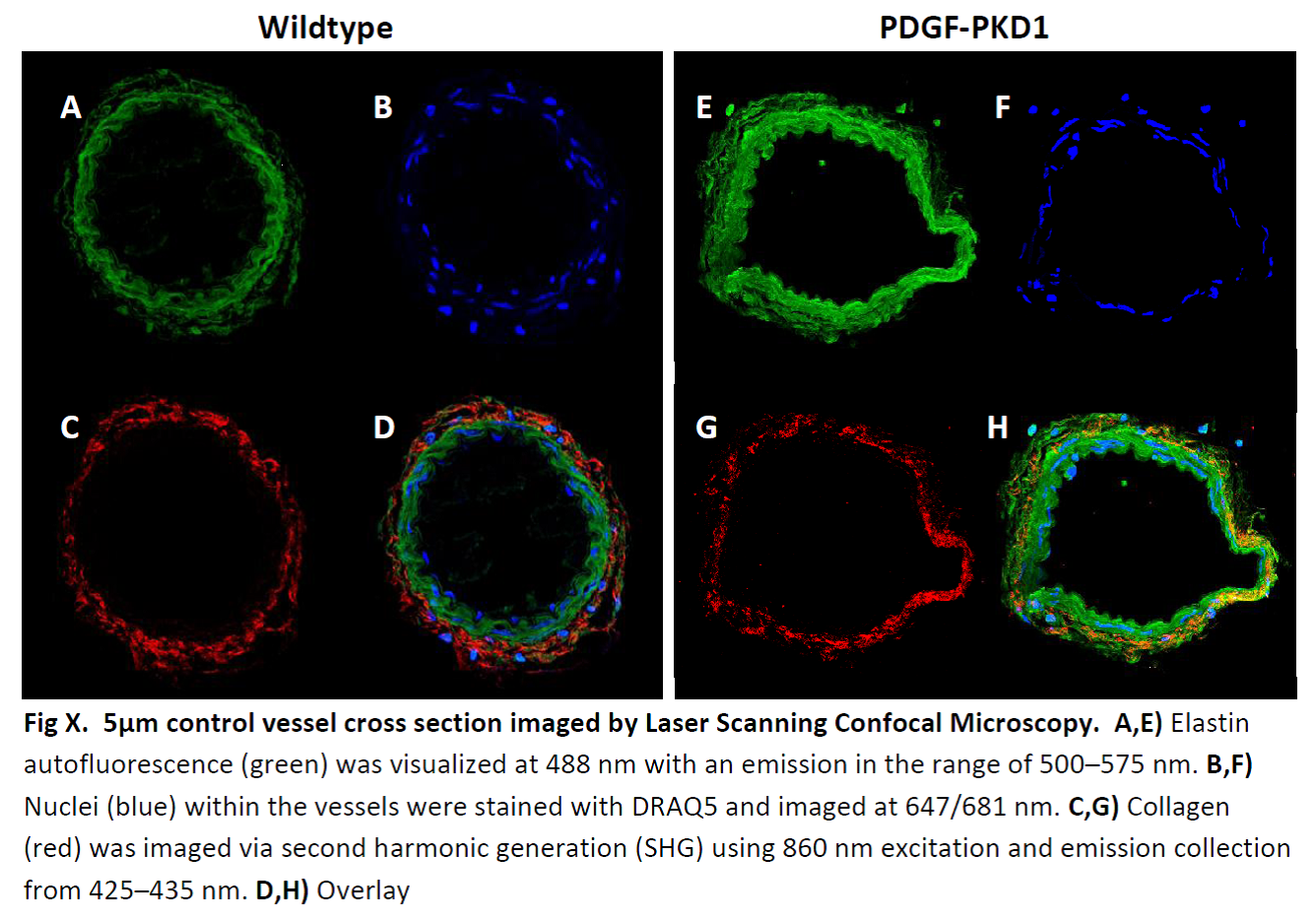
Examples of Laser scanning Confocal Microscopy in vasculature for Collagen by SHG
(red), Elastin auto-fluorescence (green) and DRAQ-5 staining of nuclei (blue) in FFPE
samples for several projects in the UToledo Advanced Microscopy & Imaging Center.
Rat abdominal aorta cross sections
 |
 |
| 10X Magnification |
63X Magnification |
Other State-of-the-Art Equipment:
CeDER laboratories have acquired several real-time PCR instruments to measure changes in gene expression in disease and in response to therapy.

To complement gene expression studies, CeDER has acquired an Odyssey Infrared protein detector system. This system provides a sensitive and an accurate means for protein detection and quantification. It also allows for the simultaneous detection of multiple proteins, while saving on the cost of reagents.

Extramural Core Facilities:
The Michigan Diabetes Research and Training Center (MDRTC) and The Proteomics Core at Wayne State University have made their core facilities available to CeDER members at the same low costs charged to MDRTC members. The following services are offered:
- Animal Phenotyping Core that includes metabolic cages and clamp analyses.
- Molecular Phenotyping Core (metabolomics services).
- Transgenic Core for generation of genetically altered mice.
- Vector Core for generation of vectors to target gene expression in live mice.
- MDRTC Chemistry Laboratory for measurement of serum metabolites and biochemistry.
- Electron Microscopy.
- Proteomics Core for characterization of protein identity and modifications.


