Factors that Affect Intoxication
There are several individual factors that may impact your intoxication level. Click
on each tab below to learn how it could factor into your level of intoxication.
 |
The more alcohol and/or the shorter the time period, the higher the BAC. |
 |
Children of an alcoholic are at a greater risk for developing alcoholism -- 4x greater!
This increased risk is sometimes described as a predisposition to alcoholism. Just
as we inherit a certain likelihood of heart disease, we are all born with some biological
level of risk for alcoholism. For some of us, that risk is increased. Those with a
biological history of alcoholism in their family is at a greater risk for alcoholism. |
 |
Males and females react to alcohol a bit differently. Women tend to be smaller than
men. Women get intoxicated faster and stay intoxicated longer. Women have less alcohol
dehydrogenase, the enzyme that metabolizes alcohol, so alcohol remains in the bloodstream
longer (in fact, men have 40% more than women). Also, women tend to have a higher
percentage of body fat, which reduces the percentage of lean body mass that can distribute
the concentration of alcohol. |
 |
Smaller stature individuals will become impaired quicker. Alcohol is distributed throughout
the body via the circulatory system, and enters most tissues except bone and fat.
This is why body composition is important, because as the percentage of body fat increases,
the resulting concentration of alcohol in the lean tissues of the body is proportionally
higher. |
 |
There are heritable components of enzyme production that have been identified. Typically,
individuals of Asian or Native American descent show reduced levels of alcohol dehydrogenase,
meaning that alcohol will remain in the blood longer and high concentrations can build
up faster. |
 |
Women who are taking some birth control pills and/or are in the premenstrual time
in their cycle may have a higher BAC. |
 |
If you are sick or just getting over an illness, you tend to become impaired more
quickly. |
 |
Strong emotions such as anger, fear, and loneliness tend to hasten impairment. The
psychological and social effects of alcohol (and the placebo effects) are also magnified
by expectations. |
 |
If you lack sleep or are tired, you will become impaired more quickly. If you get
five or less hours of sleep for four nights in a row, for example, two drinks will
start to feel like six drinks. Another way to describe this: lack of sleep reduces
tolerance, so impairment will be experienced at lower BAC levels than normal. |
 |
Food in the stomach will slow the absorption of alcohol into the bloodstream and delay
impairment. The type of food ingested (carbohydrate, fat, protein) has not been shown
to have a measureable influence on BAC. However, we do know that larger the meals,
and closer proximity to time of drinking, can lower the peak blood alcohol concentration.
This could simply be the result of the food obstructing the alcohol from entering
the bloodstream, or because the food will inhibit the stomach from emptying into the
small intestine. |
 |
Carbonation speeds up absorption. Alcohol mixed with carbonated beverages such as
Coca-Cola or tonic water will be absorbed more quickly into the bloodstream. This
is also true for champagne and wine coolers. |
 |
Energy drinks are stimulants and alcohol is a depressant. Energy drinks mask the effects
of alcohol by giving you a sense of energy and the false sense that you are not that
intoxicated. Mixing alcohol and energy drinks can cause heart failure because they
are opposing stressors on the body's regulatory systems. |
 |
Marijuana reduces nausea, which can inhibit the body's ability to remove harmful toxins
by vomiting. Marijuana can increase the threshold required to illicit a vomit response. |
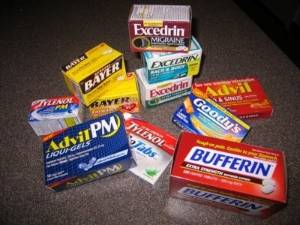 |
Do not mix alcohol with aspirin, ibuprofen (Advil), or acetaminophen (Tylenol). These
drugs are also metabolized by the liver. What you take isn't the active form, but
is transformed in the liver into the active agent. Drinking alcohol while taking painkillers
creates a "bottleneck" in the liver. The drug is processed incorrectly, the bi-products
kill liver cells, and alcohol is metabolized slower. It's also important not to mix
alcohol with other depressants, which includes some antihistamines. |
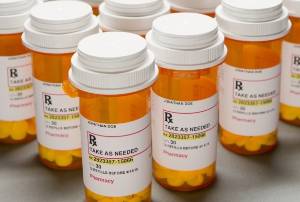 |
Mixing alcohol with prescription drugs often leads to increased or hastened impairment.
Alcohol can produce hazardous side effects, reduce heart rate, and drop blood pressure
to a dangerous level. |
*Disclaimer: This information is meant to provide education about substance use. The
content of this workshop is not meant to replace therapy and is not considered mental
health treatment. If you are in crisis or find yourself needing more support please call the UToledo Counseling Center at
419-530-2426 or dial 9-1-1 if it is an emergency.
RETURN TO ALCOHOL HOMEPAGE

















